SILICONE FLUIDS INTRODUCTION
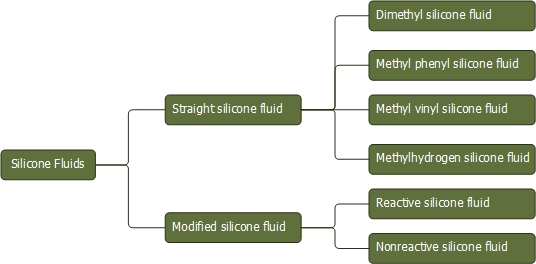
Silicone fluids are classified into two types: straight silicone
fluids and modified silicone fluids.
Silicone fluids are generally colorless transparent
liquids. They exhibit excellent resistance to heat,
cold, and moisture. There is also little viscosity
change in silicone fluids over a wide temperature
range, and they have outstanding electrical
properties. In addition, they are notable for their
characteristics of mold-releasability, water
repellency, lubricity, and defoaming properties.
Heat resistance
Silicone fluids have outstanding stability against
thermal oxidation.
Cold resistance
Silicone fluids withstand low temperatures well.
Methylphenyl silicone fluid, formulated for low
temperature applications, maintains flowability even
at -65°C.
Viscosity stability
There is little change in viscosity over a wide
temperature range.
Chemical stability
Silicone fluids are almost totally chemically inactive.
At room temperature, they show almost no effects
from alkali solutions (up to 10%) or acidic solutions
(up to 30%).
Non-corrosive and
little effect on other materials
Silicone fluids have almost no adverse effects on
metals and many other materials.
Low surface tension
Silicone fluids have much lower surface tension than
water and other common synthetic oils.
MODIFIED SILICONE FLUIDS
Modified silicone fluids are silicone fluids with additional functionality beyond the already fine properties of common dimethyl silicone fluid. This is achieved through the introduction of various organic groups. Depending on the organic group, silicone fluids can be given properties of water-solubility, compatibility or reactivity with various organic materials, paintability, and greater lubricity.
Features of dimethyl silicone fluid
· Water repellency
· Thermal oxidation stability
· Chemical stability
· Defoaming properties
Features gained through introduction of organic groups
· Paintability
· Solubility and dispersibility in water
· Compatibility or reactivity with organic materials
· Antistatic properties
· Flexibility
· Lubricity |