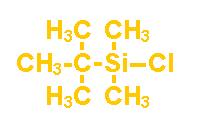CODE |
CHEMICAL
NAME |
CAS NO. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Silyl groups have long been employed to derivatize and protect various substrates
during chemical and synthetic sequences. Initial work involved derivatizing
compounds by replacing active hydrogen at-oms with silyl groups. These
classic silylation reactions have not changed appreciably over the
last de-cade. The early utilization of silylation was in the area
of analysis. The more volatile silyl derivatives of alcohols, carboxylic
acids, phenols, amino acids, carbohydrates and amines could be analyzed
through their retention times by gas chromatography. Later it was
noted that silylation had great synthetic poten-tial. Replacement
of active hydrogens with silyl groups afforded products which were
more chemically stable and would undergo subsequent chemical reactions
at sites other than the silyl blocked one. Hydrolysis would then regenerate
the unprotected functionality. A major factor contributing to the
wide acceptance of silyl blocking groups is that both blocking and
de-blocking reactions are high yield reactions and often quantitative.
This has led to the introduction of a wide range of specialty blocking
agents which have been designed for specific purposes such as selectivity,
degree of reactivity for less reactive sub-strates, nature of silylation
by product for sensitive substrates, and stability of the blocked
substrate to-wards other reagents. Some of the more prominent silylating
agents are discussed individually below.
t-Butyldimethylchlorosilane
(PC5710)
Because
of the steric bulk of the t-butyldimethylsilyl group, it is relatively
stable against de-block-ing in weakly acidic or basic media and
mild oxidizing and reducing conditions. It is unaffected by hydrogenolysis
over palladium and lithium aluminum hydride. Substrates blocked
by the t-butyldimethylsilyl group are also stable against Grignard
reagents. The stability of this blocking group has been a major
factor in developing syntheses of prostaglandins, and it has found
extensive use in terpenoid and carbohy-drate chemistry. In addition
to the foregoing, PC5710 has been utilized in the protection of
alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, phenols and other substrates.
Preparation of blocked intermediates is most satisfactorily achieved
by reaction of the substrate with PC9003 in the presence of a molar
excess of imidazole using DMF as solvent. Removal of the t-butyldimethylsilyl
group is readily accomplished through hydrolysis using acetic acid,
acetic anhydride containing FeCI3 or with tetrabutylammonium fluoride
in THF.
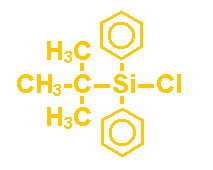
t-Butyldiphenylchlorosilane(PC8710)
This
reagent provides blocked derivatives having even greater stability
than can be achieved employing PC5710. This blocking agent is utilized
where the highest stability is desired. Hydroxyl derivatives prepared
utilizing PC8710 are stable to 80% acetic acid (which cleaves t-butyldimethylsilyl
derivatives), 50% aqueous trifluoroacetic aciddioxane, hydrogenation
over Pd, Grignard reagents and lithium alumi-num hydride. Blocked
derivatives are very resistant to hydrolysis and oxidation. Derivatization
is effi-ciently carried out using a molar excess of imidazole in
DMF solvent. Hydrolysis is effected with tetrabutylammonium fluoride
in THF.
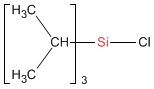
Triisopropylchlorosilane
(PC5950)
This
material has found new applications as a blocking group. It has
been utilized to prepare blocked derivatives of hydroxy compounds.
Derivatization of substrates is accomplished efficiently in DMF
containing a slight molar excess of imidazole. Blocked intermediates
exhibited acidic hydrolytic stability intermediate between that
of a PC5710 and PC8710 derivatives. Greater stability was obtained
with PC5950 under basic conditions. With n-butyl alcohol as the
substrate, the following half-life stabilities were recorded.
| Blocking Reagent |
H |
OH |
| PC5710 |
<1min |
1h |
| PC5950 |
18min |
14h |
| PC8710 |
244min |
<14h |
Deblocking
is achieved by reaction with tetrabutylammonium fluoride in THF.
 Power Chemical Corporation - SiSiB® SILANES (Full Catalogue, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9, P10)
Power Chemical Corporation - SiSiB® SILANES (Full Catalogue, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9, P10)